Threat intelligence is a core component of a Zero Trust (ZT) architecture. ZT is a security concept and framework that assumes that all network traffic is to be untrusted and requires strong authentication and authorization. Threat intelligence can then be used to support the development and implementation of zero trust policies and controls.
Threat intelligence can help an organization identify and better assess potential threats and risks to systems and networks. Threat intelligence can be used to identify previously known threat actors and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) they use. Threat intelligence can also identify emerging threats which may not be previously identified. This valuable information can be used to further enhance security controls to better monitor for related suspicious activity within the network.
| The NIST SP 800-207 specification on the Zero Trust Architecture Framework overviews the important role of threat intelligence in a ZT architecture. According to NIST SP 800-207, threat intelligence is a core component of a Zero Trust architecture. |
A simple example would be where an organization has used threat intelligence to identify a threat actor and the malicious malware tools they use, so that the security controls in place can utilize that threat intelligence to detect and successfully block that malware from entering the network.
Threat intelligence can also be used to educate and train employees on how they identify and best respond to possible threats. In a ZT network environment, all network traffic must be assumed to be untrusted, so employees are expected to be watchful for potential suspicious activity. ZT helps organizations understand and identify threats earlier, and then inform the development and deployment of more effective security controls.
NIST SP 800-207 on Zero Trust Architecture
Threat intelligence helps organizations understand likely and potential threats to their organization. Further, threat intelligence can inform the implementation of effective security controls. NIST SP 800–207 notes that “threat intelligence can be used to identify known malicious actors and their TTPs, as well as emerging threats not previously known.”
Here you can see in the NIST SP 800-207 Figure 2 graphic that threat intelligence is identified as a core ZT logical component:
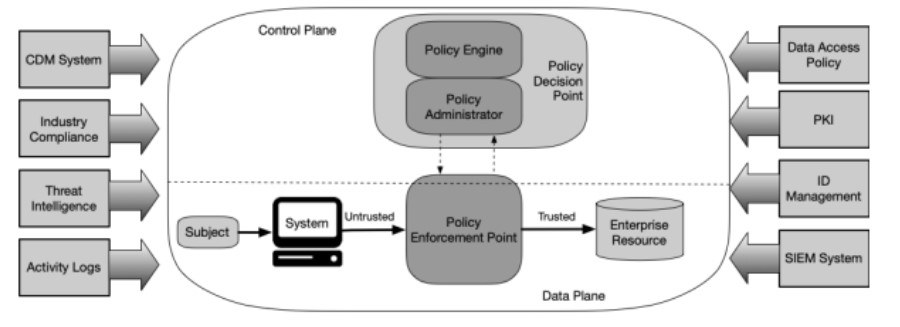
Figure 12: ZTA Deployment Cycle
It is important to incorporate threat intelligence into a ZT architecture such that it is scalable, automated, and well-integrated with other security controls NIST SP 800-207 further recommends that organizations establish a process to collect, analyze, and disseminate threat intelligence. This process should also be well-integrated with other security controls such as network segmentation and access control.
Infoblox Threat Intelligence – An Essential Part of Your Zero Trust Strategy
Infoblox threat intelligence can be used to support a zero trust architecture by providing organizations with real-time visibility into potential threats to their systems and networks. This can be accomplished through the use of threat feeds, which provide up-to-date information on known malicious actors and their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This threat feed information can be used to inform the development and implementation of security controls that are designed to detect and block potential threats from entering the network.
Infoblox threat intelligence can also be used to enhance network segmentation and access controls within a zero trust architecture. For example, Infoblox can be used to monitor for suspicious activity on the network and alert security teams to potential threats. This can help organizations identify and respond to potential threats in a timely manner, reducing the risk of a successful attack.
In support of threat intelligence data and analysis, Infoblox also offers the Threat Intelligence Data Exchange (TIDE) platform and the Dossier threat investigation research and analysis tool. The TIDE platform can automate the incoming flow, management and distribution of threat intelligence. TIDE can also support the use of additional feeds from a wide variety of sources, both internal and external. Dossier enables analysts to rapidly gain deep knowledge of available threat intelligence, so they can more quickly assess data and reach confident conclusions faster. Dossier provides immediate access to important data such as threat severity, WHOIS data, MITRE ATT&CK guidance, related IPs/URLs/Domains, file samples, timelines, threat actor backgrounds, and more.
Both TIDE and Dossier are important in supporting a ZT architecture by providing organizations with the information they need to identify and respond to potential threats quickly and effectively. By understanding the nature and origins of potential threats, organizations can better inform the development and implementation of security controls designed to detect and block them from entering the network. In this way, TIDE and Dossier can help organizations better protect their systems and networks within a zero trust environment.
For more information on Infoblox Threat Intelligence: Infoblox Threat Intelligence | Strengthen Your Entire Security Portfolio
To know more, please reach out to us directly via https://info.infoblox.com/contact-form/.