The public cloud offers operational best practices, automation efficiencies, scalability, virtually unlimited capacity, infrastructure cost advantages, pay-as-you-go pricing consistency, and favorable user experience. There are many important factors to consider as you develop your cloud strategy to achieve these benefits. One area includes the practical capabilities that will give your organization an advantage when deploying services in the hybrid cloud. This blog highlights how Infoblox vNIOS can be used to solve six essential use cases for optimizing the value of your cloud infrastructure investment.
DNS for Hybrid Cloud
DNS is a great place to start. A vNIOS appliance, used as the primary DNS server in Azure VNets and GCP / AWS VPCs, extends your enterprise DNS and RPZ services into the public cloud. Clients attached to your VPCs and VNets running on these cloud platforms can use the same consolidated, secure DNS service as clients on-premises and in your private cloud environments. Plus, vNIOS appliances can be used for DNS resolution when running the DNS service in shared services or virtual networks, and even across other virtual networks via peering relationships. When combined with vDiscovery, this can be especially powerful for automatically creating DNS records for your Azure, AWS, and GCP VMs (see Fig. 1).
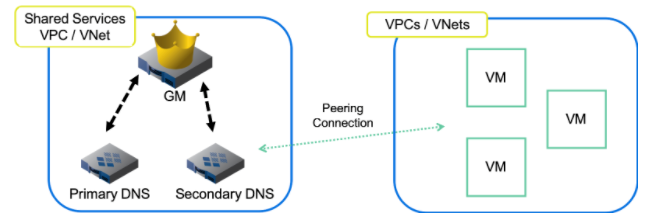
Figure 1
DNS, Discovery, and IPAM for Cloud Resources
The automatic discovery of cloud resources is another critical use case (see Figs. 1 and 2). Organizations often manage dynamic hybrid and multi-cloud environments, frequently creating, revising, and terminating accounts, subscriptions, and VMs. With so many changes, it can be challenging to keep track. Infoblox solves this problem automatically using the vNIOS appliance with vDiscovery and Cloud Network Automation (CNA). Tasks can run so that the vNIOS appliance automatically detects, captures, stores, and syncs Tenant, VNET / VPC, and VM data from your public cloud environments into an authoritative IPAM database. With all of the network endpoints synced into a central, viewable database, users gain full visibility into all cloud environments, confidence in an accurate, authoritative, real-time data set, and a single efficient control plane to manage hybrid, multi-cloud resources (see Fig. 2).
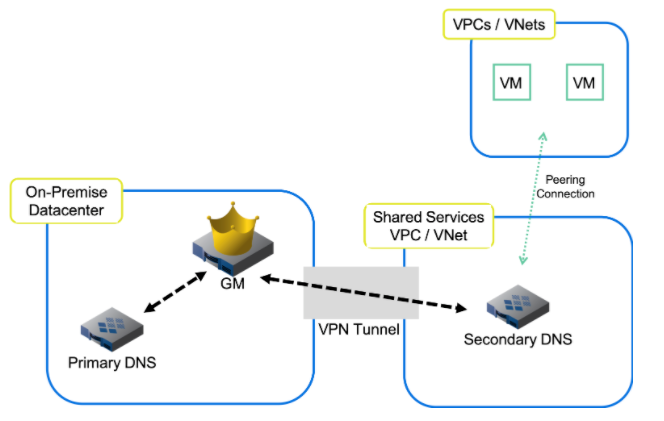
Figure 2
Fault Tolerance and Disaster Recovery
Fault tolerance and disaster recovery are two additional core network services use cases. By deploying vNIOS appliances in public cloud environments, you can gain fault tolerance even if one or more of your cloud components fail, and aid in Disaster Recovery of DNS, DHCP and IPAM services (see Fig. 3). Further, should you encounter a critical failure in your primary datacenter (e.g., due to a power or network outage), an Infoblox vNIOS appliance enabled as a Grid Master Candidate (GMC) can be quickly promoted to the Grid Master role to continue Grid services. Moreover, deploying vNIOS appliances in multiple regions across multiple public clouds can even further increase fault tolerance, resiliency, and survivability. You can also run DNS services automatically without manual intervention in the public cloud to ensure business continuity. Finally, DHCP fault tolerance can use Infoblox DHCP failover between on-premises grid members and members running on AWS, to enable continued operations in the event servers become unavailable.
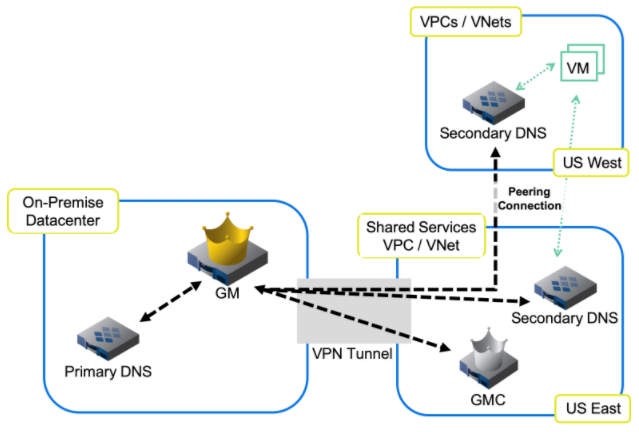
Figure 3
High Availability
In a distributed, geo-diverse, hybrid cloud environment, it is essential to ensure that services and resources are available on demand. You can deliver Highly Available (HA) DDI services by deploying vNIOS appliances in the public cloud using Availability Sets or Zones. Thus, you can ensure availability even in the event of unplanned service interruptions or maintenance and enables you to optimize uptime Service Level Agreements offered by public cloud providers. Further, by deploying vNIOS appliances into “shared service” or “transit” VPCs/VNets, you can be confident about uptime across all virtual networks. Finally, using peering connections, virtual networks can be connected for maximum availability.
API Survivability and Scalability
Using the Infoblox Cloud Platform (CP) appliance delivers survivability and scalability for API services (see Fig. 4). The CP appliance deployed on a public cloud platform can accept API calls from branch offices and edge locations. Moreover, the CP appliance will continue to receive API calls even if your primary data center or Infoblox Grid Master becomes unavailable. It’s easy to improve access and scale-out API performance by installing multiple CP appliances in areas near your branch locations.
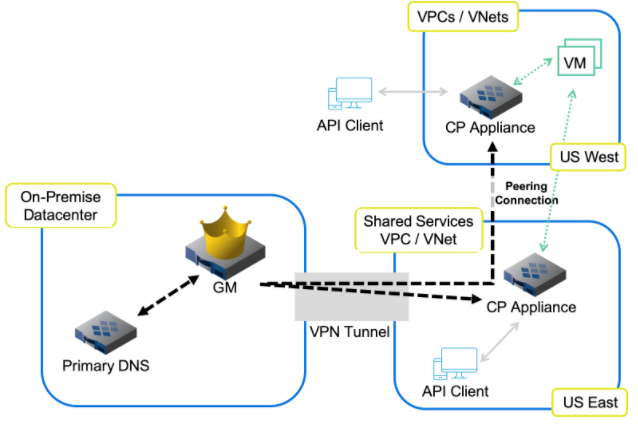
Figure 4
DHCP AWS Service for On-Premises Clients
For organizations running on AWS environments, a vNIOS appliance can provide DHCP service for on-premises clients (see Fig. 5). A vNIOS DHCP appliance can serve as your primary DHCP server or as part of a failover pair, with a NIOS DHCP server running on-premise for a hybrid, survivable solution. Two vNIOS appliances, each running in AWS, can also serve as a DHCP failover for highly available, fault-tolerant DHCP services. Using a vNIOS appliance running on AWS for DHCP requires using DHCP Relay or IP Helper on your router or layer-3 switch to send DHCP traffic from your on-premise network to your AWS VPC.
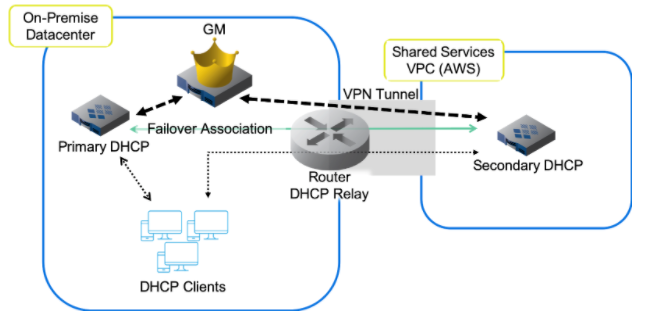
Figure 5
So, whether you’re already there, or you’re looking to gain core network automation efficiencies, scalability, capacity, cost advantages, pricing consistency, and ultimately, a better user experience, deploying your services in the public cloud makes sense. Once you’re there, consider adding DNS, DHCP and IPAM, discovery, high availability, API survivability and scalability, and DHCP service for on-premises AWS clients to optimize your public cloud strategy and investment. For more information, contact your Infoblox Account Team or System Engineer.